The Role of Carving in Restoring Ancient Cultural Artifacts
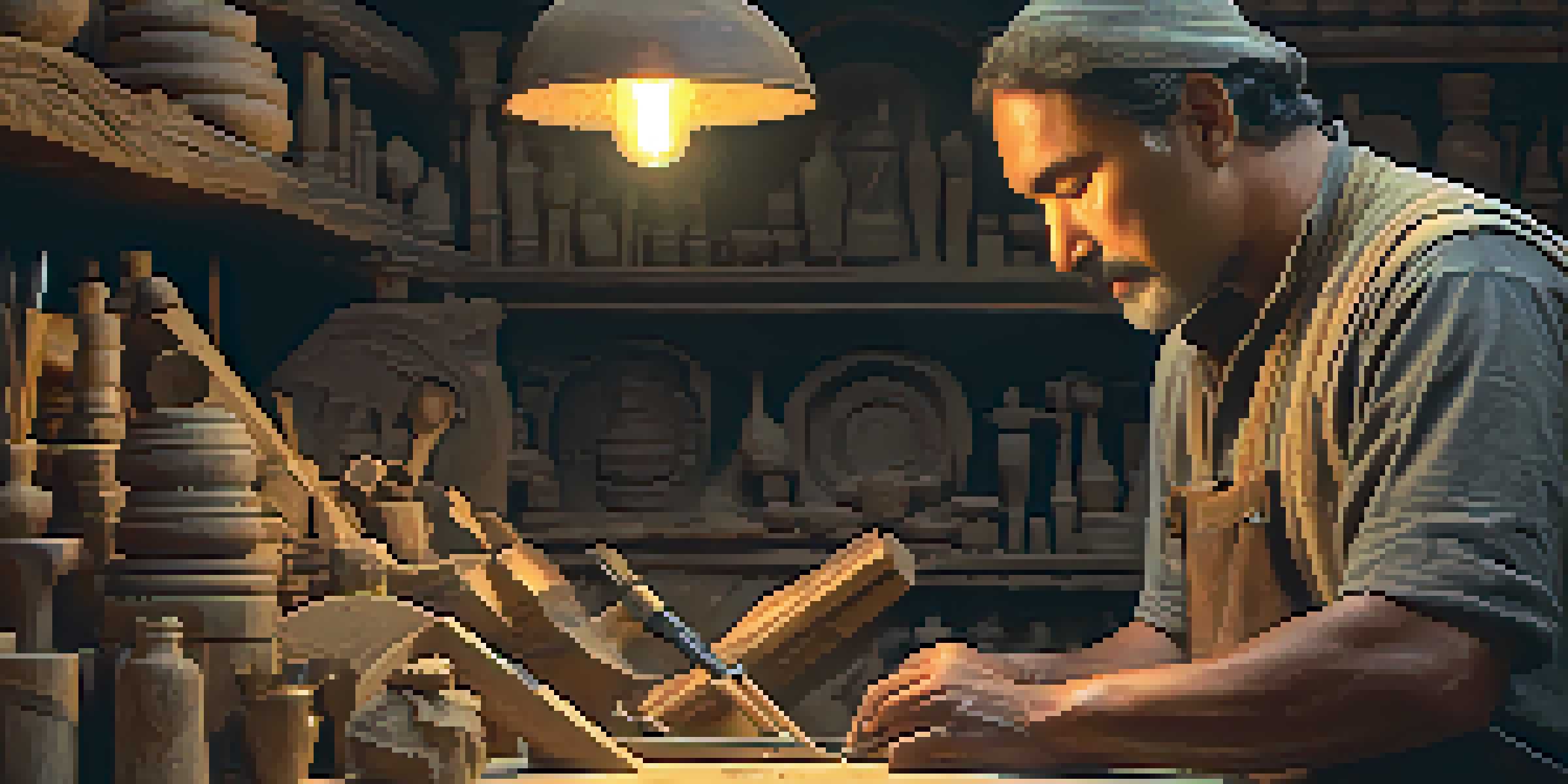

Understanding the Importance of Cultural Artifacts
Cultural artifacts are tangible links to our past, offering insights into the lives of ancient civilizations. They include everything from pottery and sculptures to tools and textiles, each telling a unique story. Preserving these artifacts is crucial, as they help us understand historical contexts, traditions, and artistic expressions.
Preservation of our cultural heritage is not just about saving objects; it's about saving our stories.
However, time can be unforgiving. Artifacts often suffer from wear and tear due to environmental factors, human interaction, and natural degradation. This is where restoration comes into play, aiming not only to preserve these items but also to ensure that future generations can appreciate them.
Among various restoration techniques, carving holds a significant role. It helps to repair or recreate missing parts of an artifact, ensuring that the final product remains true to its original form while also being safe for display.
The Art of Carving: A Restoration Technique
Carving in the context of artifact restoration involves carefully shaping materials to match the original piece's design and texture. This delicate process requires not just skill but also a deep understanding of the artifact’s historical context. Restoration experts often study photographs, sketches, and relevant literature to guide their work.
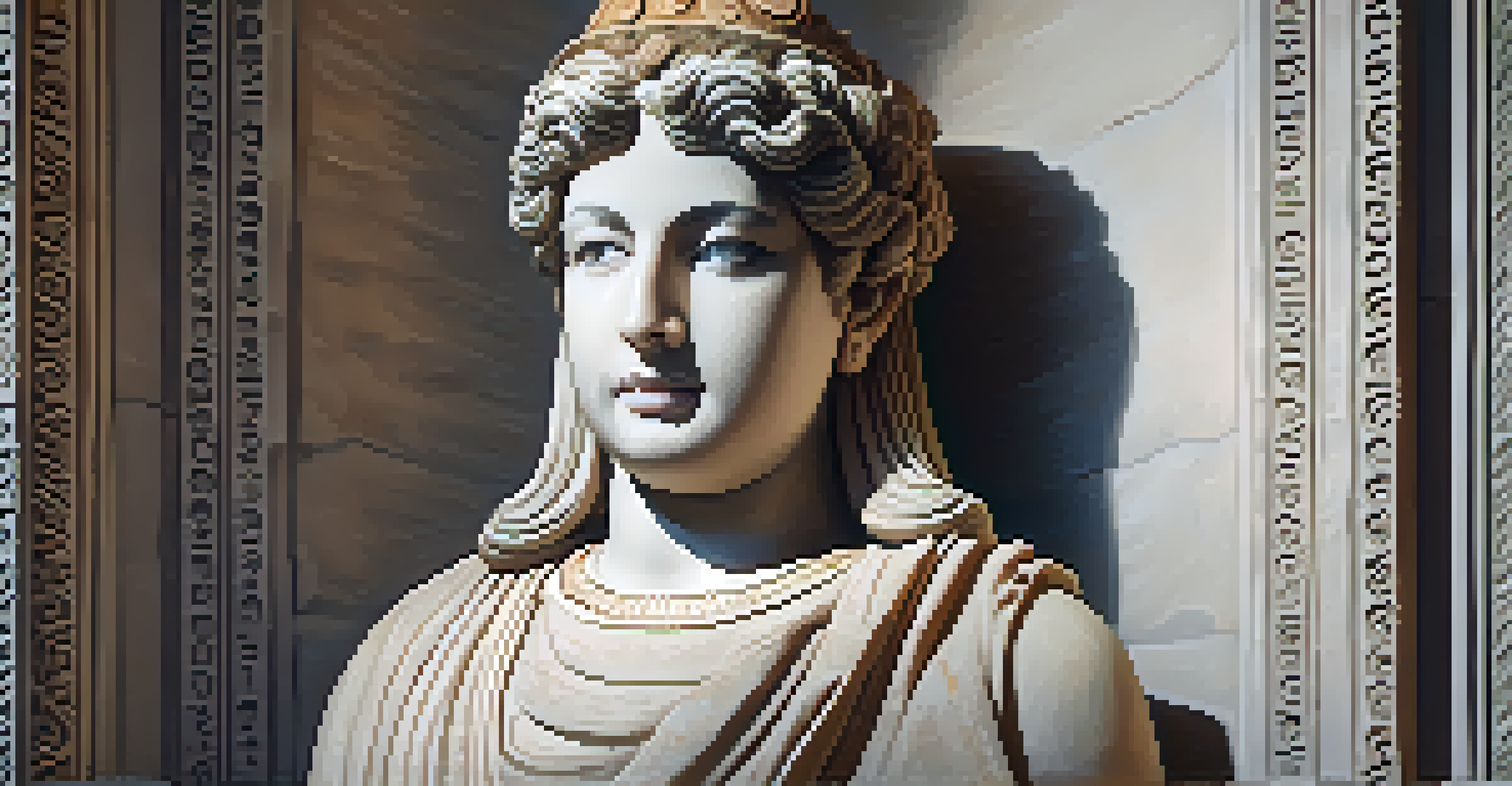

For instance, when restoring a damaged statue, a skilled carver may use tools to replicate the original details, such as facial features or intricate patterns. This meticulous attention to detail ensures that the restoration is both aesthetically pleasing and respectful of the original work.
Cultural Artifacts Connect Us to History
Cultural artifacts serve as vital links to our past, providing insights into the lives, traditions, and artistic expressions of ancient civilizations.
Moreover, the materials used for carving are chosen carefully to match the original artifact closely. This compatibility is crucial in avoiding further damage to the artifact over time, ensuring that it remains a part of our cultural heritage.
Challenges Faced in Carving Restorations
While carving is a vital tool in restoration, it comes with its own set of challenges. One of the primary concerns is maintaining the integrity of the original artifact. Restorers must balance the need for repairs with the importance of preserving as much of the original material as possible.
The past is not dead; it is not even past.
Another challenge is the potential for misinterpretation. If a restorer lacks sufficient knowledge about the artifact's history or artistic style, they may inadvertently alter its significance. This emphasizes the need for collaboration among historians, archaeologists, and conservators during the restoration process.
Lastly, the emotional aspect can’t be overlooked. Artifacts often hold cultural significance, and there is a responsibility to treat them with respect and care. Carving requires not only technical skill but also a sensitivity to the artifact's story and meaning.
Case Studies: Successful Carving Restorations
Several notable restorations highlight the effectiveness of carving techniques. One famous example is the restoration of the Parthenon Marbles, where skilled conservators used carving to fill in missing pieces while ensuring the new material blended seamlessly with the original.
Another instance is the restoration of ancient Egyptian artifacts, such as statues and reliefs, where carving was used to recreate lost details. These efforts not only helped in preserving the artifacts but also enhanced their usability for educational purposes.
Carving is Key in Restoration Efforts
The technique of carving plays a crucial role in restoring artifacts, ensuring that missing parts are accurately replicated while preserving the original's integrity.
These case studies illustrate the profound impact of skilled carving in the restoration field, demonstrating how it can breathe new life into historical pieces while maintaining their authenticity.
The Role of Technology in Modern Carving Techniques
With advancements in technology, the art of carving has evolved significantly. Tools such as laser engraving and 3D printing are now being utilized in restoration projects, allowing for more precise and less invasive repairs. These technologies can replicate intricate details that might be difficult to achieve through traditional methods.
For example, laser technology can analyze the original surface of an artifact, capturing minute details that can be reproduced during the restoration process. This not only preserves the artifact's integrity but can also enhance its visual appeal.
While these technologies offer exciting possibilities, they also raise ethical questions about authenticity and the definition of restoration. It's crucial to find the right balance between innovation and tradition in the preservation of our cultural heritage.
Ethical Considerations in Carving Restorations
Carving in restoration is not solely a technical endeavor; it also involves ethical considerations. One significant aspect is transparency. Restorers must document their processes and the materials used so that future generations can understand the work that has been done.
Moreover, there is the question of intervention. How much restoration is too much? Some experts advocate for minimal intervention, preserving artifacts as they are, while others believe in restoring them to their former glory. This ongoing debate highlights the complexity of restoration ethics.
Ethics Shape Restoration Practices
The restoration process involves ethical considerations, including transparency and the debate over the extent of intervention, to honor the artifact's history.
Ultimately, the goal is to honor the artifact's history and significance. Respecting the original work while making it accessible to a broader audience is a delicate balance that restorers strive to achieve.
The Future of Carving in Artifact Restoration
As we look to the future, the role of carving in restoring cultural artifacts is likely to expand. With ongoing advancements in materials science and technology, restorers will have more tools at their disposal to tackle even the most challenging restorations.
In addition, there is a growing interest in interdisciplinary approaches, where collaboration among artists, historians, and scientists can lead to innovative restoration techniques. This fusion of knowledge can enrich the restoration process and result in more authentic reproductions.
The continued importance of education and training in carving techniques will also play a crucial role. By equipping the next generation of conservators with the skills and knowledge they need, we can ensure that our cultural heritage is preserved for years to come.