Exploring the Subtle Differences Between Sculpture and Carving
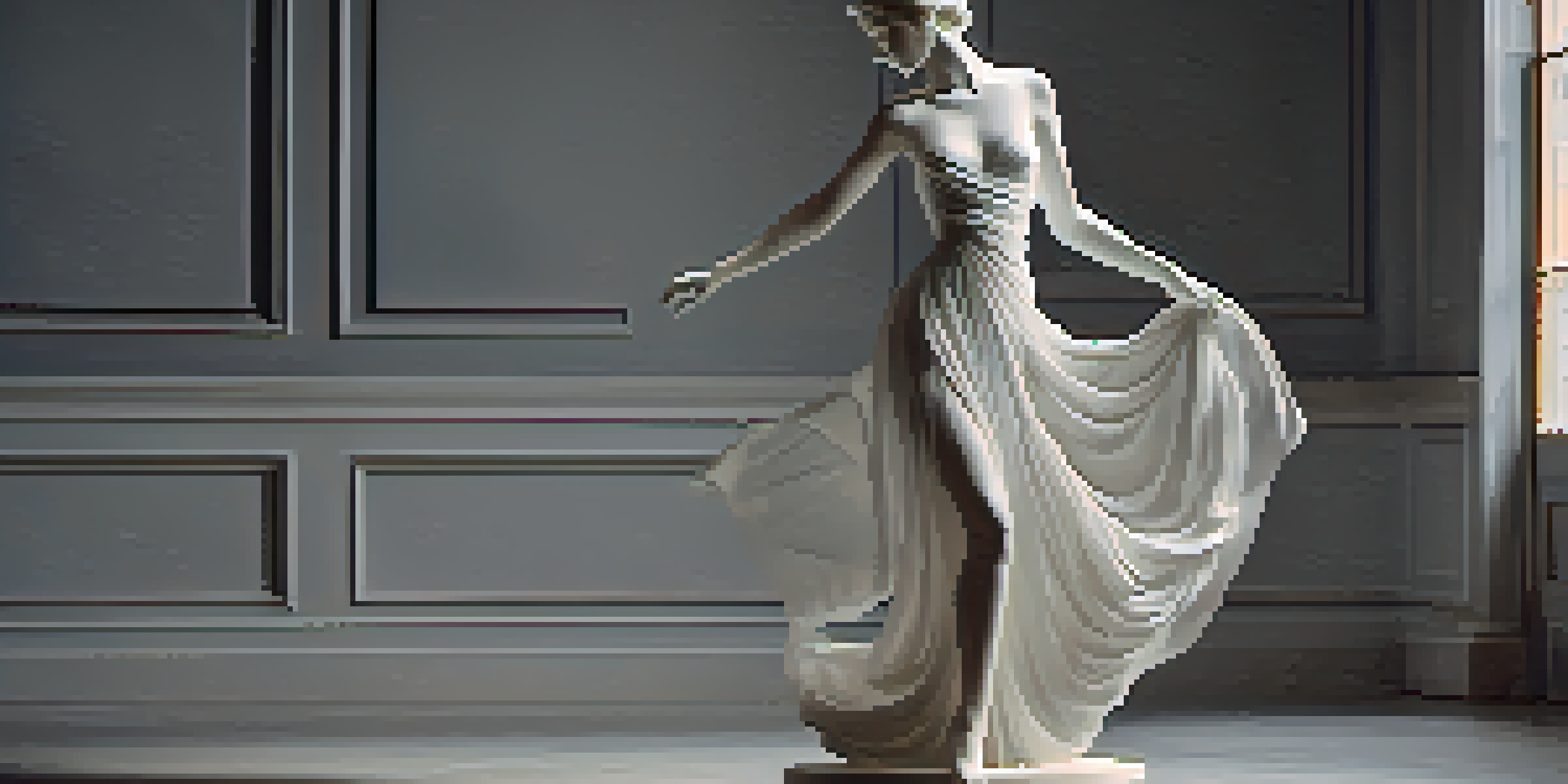

Defining Sculpture: A Broad Artistic Category
Sculpture is an expansive art form that encompasses various techniques and materials. It involves the creation of three-dimensional artworks, allowing for a diverse range of expressions, from figurative to abstract. Artists can work with mediums like clay, metal, stone, or even found objects, which gives sculpture its rich variety.
Sculpture is the art of the intelligence, and we must not forget that it is also a language that speaks to the soul.
One of the beautiful aspects of sculpture is its ability to capture movement and emotion in a tangible form. Think of Michelangelo’s David or a modern installation piece—their physical presence can evoke powerful reactions. This versatility is what sets sculpture apart as a unique artistic endeavor.
In essence, sculpture is about creating forms that can be appreciated from multiple angles, engaging viewers in a way that flat art cannot. Whether it’s a grand statue or a delicate bust, sculpture invites us to walk around and explore its details, making it a dynamic part of the art world.
Carving: A Specific Technique in Sculpture
Carving is a particular method within the broader category of sculpture, primarily focused on subtractive techniques. This means that artists remove material from a solid block, be it wood, stone, or ivory, to reveal the final form. The process requires both skill and patience, as each cut is permanent.
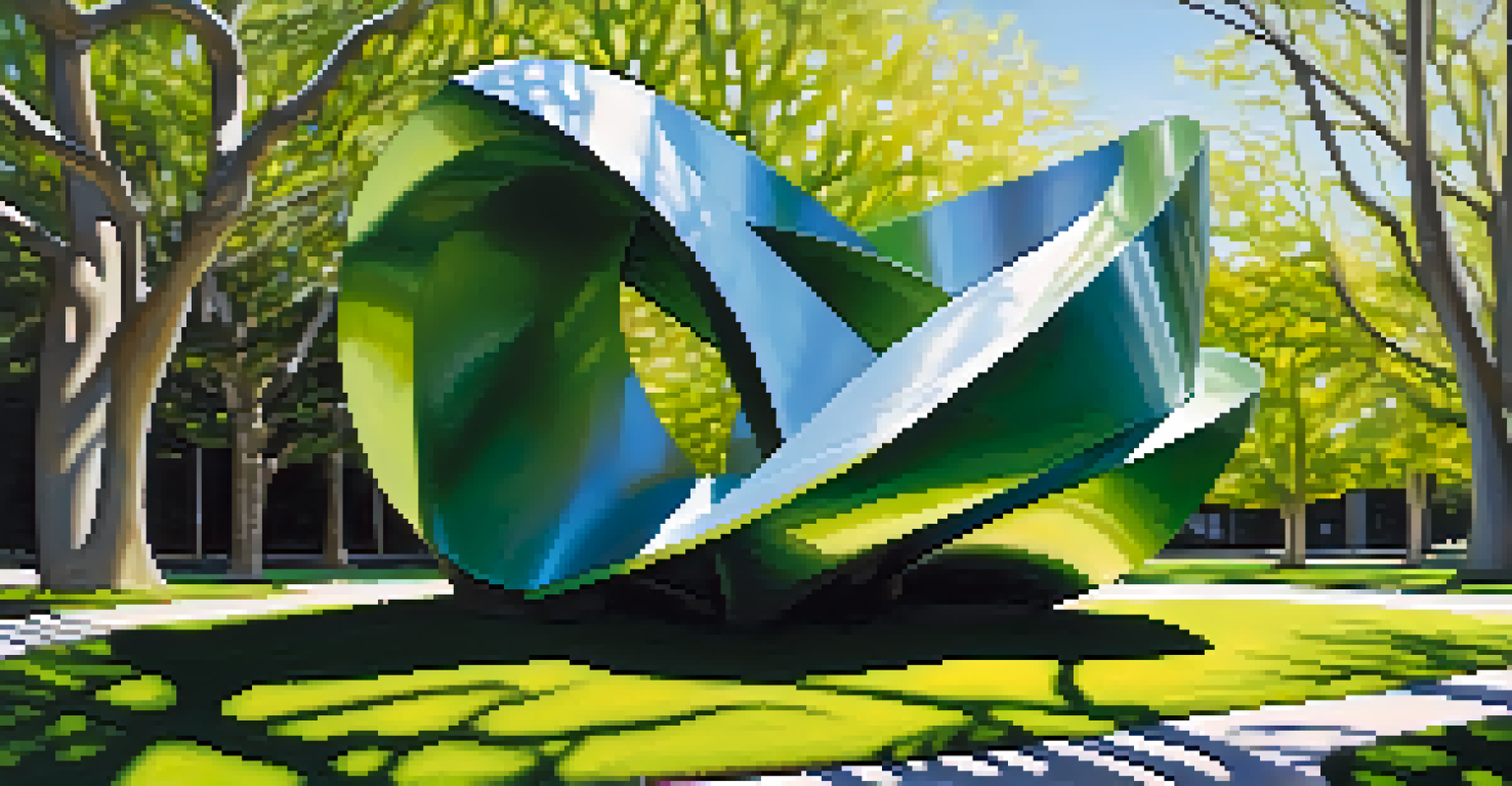
Imagine starting with a sturdy block of marble, chipping away at it gradually until a figure emerges—this is the essence of carving. Artists must have a clear vision of the final piece in their minds, as every decision shapes the outcome. The precision and care involved in carving can lead to stunningly intricate details.
Sculpture: A Multifaceted Art Form
Sculpture encompasses various techniques and materials, allowing for diverse expressions from figurative to abstract.
In summary, while all carving is sculpture, not all sculpture is carving. This distinction highlights the specific focus on material removal in carving, contrasting with other techniques like modeling or casting that may add or mold materials instead.
Materials Matter: The Choices Sculptors Make
Both sculpture and carving involve a variety of materials, each influencing the final artwork's look and feel. Sculptors may choose stone for its durability, clay for its malleability, or metal for its modern appeal. These choices significantly impact the sculpting process and the viewer's experience.
The sculptor's art is to make the invisible visible.
For instance, a stone sculpture often exudes a sense of permanence and timelessness, while a clay piece might feel more approachable and intimate. The texture, weight, and color of the materials can alter our perception, making material selection a critical aspect of the artistic process.
Ultimately, the material speaks alongside the form. A carved wooden figure may evoke warmth and familiarity, while a polished bronze piece might convey elegance and sophistication. Understanding these materials helps us appreciate the nuanced differences between various sculptural works.
Techniques: Carving vs. Other Sculptural Methods
While carving emphasizes removing material, other sculptural methods, like modeling, involve adding and shaping materials. For example, in modeling, artists typically manipulate soft substances like clay to create forms, which can then be hardened through firing or casting. This creates a distinct process of building rather than subtracting.
Additionally, casting allows for the duplication of sculptures using molds, enabling artists to produce multiple versions of a single piece. This method contrasts with carving, where each piece is unique and cannot be replicated identically. These varying techniques illustrate the diverse approaches within the realm of sculpture.
Carving vs. Other Techniques
Carving involves subtracting material to create forms, contrasting with techniques like modeling and casting that build or replicate.
In a way, approaching sculpture is like choosing between a sculptor's chisel and a potter's wheel; each tool leads to different outcomes and artistic expressions. The choice of technique not only defines the process but also influences the emotional impact and physical presence of the artwork.
Cultural Significance: Sculpture Across Time
Sculpture has been an integral part of human culture for millennia, reflecting societal values, beliefs, and advancements. From ancient civilizations that carved intricate statues for worship to modern artists pushing the boundaries of form and material, sculpture has evolved alongside humanity. This evolution showcases how art can mirror the changing world.
Many cultures have their unique sculptural traditions, such as the detailed carvings of ancient Egypt or the intricate wood sculptures of Indigenous peoples. These works often serve not only aesthetic purposes but also functional and ritualistic roles within their respective communities. This cultural significance highlights the importance of sculpture in human history.
Understanding the cultural context of sculpture enriches our appreciation for the art form. Each piece tells a story, connecting us to the people and times that produced it, and this dialogue between the past and present continues to influence contemporary sculptors today.
The Emotional Connection: Viewer Experience
One of the most compelling aspects of both sculpture and carving is their ability to evoke emotions in viewers. The physical presence of a three-dimensional piece can create a sense of intimacy, drawing people in and encouraging them to explore the artwork from different perspectives. This interaction can lead to a profound connection, as viewers often find personal meanings in the forms.
For example, a carved figure may resonate with someone due to its expressive features, while a large abstract sculpture might inspire feelings of wonder and curiosity. These emotional responses are part of what makes sculpture such a powerful art form, transcending language and cultural barriers.
Cultural Impact of Sculpture
Throughout history, sculpture has reflected societal values and beliefs, showcasing its significance across different cultures.
In essence, the experience of viewing sculpture can be transformative. It invites us to pause, reflect, and engage with the artwork on a deeper level, forging connections that go beyond mere observation.
The Future of Sculpture: Innovation and Tradition
As we move forward, the world of sculpture continues to evolve, blending traditional techniques with innovative approaches. Contemporary artists are experimenting with new materials, technologies, and concepts, pushing the boundaries of what sculpture can be. This experimentation often leads to surprising and thought-provoking works that challenge our perceptions.
For instance, some artists are incorporating digital technology into their processes, using 3D printing to create intricate forms that were once unimaginable. Others are exploring environmental themes, using recycled materials to make statements about sustainability. These trends illustrate how the art form remains relevant and responsive to contemporary issues.

Ultimately, the future of sculpture is a vibrant tapestry woven from tradition and innovation. As artists explore new avenues, they honor the past while shaping a dynamic future, ensuring that sculpture remains a vital part of the artistic landscape.